Adopting existing clusters to use ClusterClass
Learn how to adopt your existing CAPI cluster to use ClusterClass.
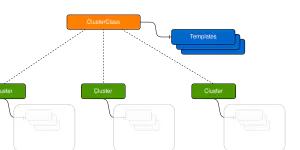
What Is ClusterClass?
The ClusterClass feature is an important evolution of the Cluster API project. Although it is still an alpha feature, CAPI core and many of the infrastructure providers are working hard to provide support for it. You can read more about the different motivation and goals of ClusterClass in the original proposal, but the one I’m most excited for is declarative Kubernetes version upgrades.
When performing a regular Cluster API cluster upgrade, you must have something that will sequentially trigger an upgrade of the control-plane, wait for that upgrade to complete, start the upgrade of each of your MachineDeployments and wait for those to finish. ClusterClass greatly simplifies this flow, by letting you change a single version value in the Cluster object and having the new topology reconcile the change for use in the correct order across the whole cluster.
In this post, I will show you how to adopt an existing Cluster API Docker (CAPD) cluster to use the ClusterClass feature. You can apply the same steps for any of your clusters as long as they are using CABPK and MachineDeployments.
Create a CAPD Cluster
Create a bootstrap cluster by following the Quickstart.
Deploy the
dockerinfrastructure provider:Create the base CAPD cluster:
Fetch the kubeconfig for the CAPD cluster:
1clusterctl get kubeconfig $CLUSTER_NAME > $CLUSTER_NAME.confIf you are using macOS you can update the generated kubeconfig with the correct
serveraddress:Deploy Calico CNI:
1kubectl --kubeconfig $CLUSTER_NAME.conf apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.24.1/manifests/calico.yaml
After a few minutes all the Nodes will become Ready.
Adopt the CAPD Cluster
At a high level, we will:
- Create a
ClusterClassresource specific to our cluster, and missing templateDockerClusterTemplateandKubeadmControlPlaneTemplateresources. - Annotate, label, and patch existing cluster resources with required values to what the topology controller expects it to be.
- Patch the
Clusterobject to use the newClusterClass.
Create New Resources
Create a
ClusterClassresource with the same$CLUSTER_NAME:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: ClusterClass metadata: name: ${CLUSTER_NAME} namespace: ${NAMESPACE} labels: cluster.x-k8s.io/provider: docker spec: controlPlane: ref: apiVersion: controlplane.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: KubeadmControlPlaneTemplate name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-control-plane machineInfrastructure: ref: kind: DockerMachineTemplate apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1 name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-control-plane infrastructure: ref: apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: DockerClusterTemplate name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-cluster workers: machineDeployments: - class: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-md-0 template: bootstrap: ref: apiVersion: bootstrap.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: KubeadmConfigTemplate name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-md-0 infrastructure: ref: apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: DockerMachineTemplate name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-md-0 EOFCreate
DockerClusterTemplateandKubeadmControlPlaneTemplateresources. You will want to base these on the specs ofDockerClusterand theKubeadmControlPlaneof your cluster:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: DockerClusterTemplate metadata: name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-cluster spec: template: spec: controlPlaneEndpoint: host: 172.19.0.3 port: 6443 loadBalancer: {} --- kind: KubeadmControlPlaneTemplate apiVersion: controlplane.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-control-plane namespace: ${NAMESPACE} spec: template: spec: kubeadmConfigSpec: clusterConfiguration: apiServer: certSANs: - localhost - 127.0.0.1 - 0.0.0.0 controllerManager: extraArgs: enable-hostpath-provisioner: 'true' dns: {} etcd: {} networking: {} scheduler: {} format: cloud-config initConfiguration: localAPIEndpoint: {} nodeRegistration: criSocket: /var/run/containerd/containerd.sock kubeletExtraArgs: cgroup-driver: systemd eviction-hard: nodefs.available<0%,nodefs.inodesFree<0%,imagefs.available<0% joinConfiguration: discovery: {} nodeRegistration: criSocket: /var/run/containerd/containerd.sock kubeletExtraArgs: cgroup-driver: systemd eviction-hard: nodefs.available<0%,nodefs.inodesFree<0%,imagefs.available<0% EOF
Annotate, Label, and Patch Cluster Resources
A webhook will disallow adding the topology section to an existing cluster, add this annotation to disable webhook check:
1kubectl annotate cluster $CLUSTER_NAME unsafe.topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/disable-update-class-name-check=Label the cluster resources with what the topology controller expects it to be. Replace
$CLUSTER_NAME-control-planeand$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0with the names of your control-plane andMachineDeployment:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31# label cluster kubectl label Cluster/$CLUSTER_NAME topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= kubectl label DockerCluster/$CLUSTER_NAME topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= # label resources based on the cluster label kubectl label MachineSet -l cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name=$CLUSTER_NAME topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= kubectl label DockerMachine -l cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name=$CLUSTER_NAME topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= kubectl label Machine -l cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name=$CLUSTER_NAME topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= kubectl label KubeadmConfig -l cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name=$CLUSTER_NAME topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= # label control-plane kubectl label DockerMachineTemplate/$CLUSTER_NAME-control-plane topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= kubectl label DockerMachineTemplate/$CLUSTER_NAME-control-plane cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name=$CLUSTER_NAME kubectl label KubeadmControlPlane/$CLUSTER_NAME-control-plane topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= kubectl label MachineSet -l cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-control-plane topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-control-plane kubectl label Machine -l cluster.x-k8s.io/control-plane-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-control-plane topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-control-plane kubectl label DockerMachine -l cluster.x-k8s.io/control-plane-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-control-plane topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-control-plane # label worker nodepool kubectl label DockerMachineTemplate/$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= kubectl label DockerMachineTemplate/$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name=$CLUSTER_NAME kubectl label DockerMachineTemplate/$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 kubectl label KubeadmConfigTemplate/$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= kubectl label MachineDeployment/$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned= kubectl label MachineDeployment/$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 kubectl label KubeadmConfig -l cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 kubectl label MachineSet -l cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 kubectl label Machine -l cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 kubectl label DockerMachine -l cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0 topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name=$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0Patch the worker
MachineSetwith new labels. This prevents the topology controller from recreating the existing Machines. Replace$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0with the name of yourMachineDeployment:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21cat <<EOF > machineset-patch.json { "spec": { "selector": { "matchLabels": { "topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name": "$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0", "topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned": "" } }, "template": { "metadata": { "labels": { "topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/deployment-name": "$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0", "topology.cluster.x-k8s.io/owned": "" } } } } } EOF kubectl patch $(kubectl get machineset -l cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name=$CLUSTER_NAME -o name) --type merge --patch-file machineset-patch.json
Set Topology Values for the Cluster
Create a Cluster patch file, setting the
replicasand theversionto your cluster’s current Kubernetes version:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21cat <<EOF > cluster-patch.json { "spec": { "topology": { "class": "$CLUSTER_NAME", "controlPlane": { "metadata": {}, "replicas": 1 }, "version": "$KUBERNETES_VERSION", "workers": { "machineDeployments": [{ "class": "$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0", "name": "$CLUSTER_NAME-md-0", "replicas": 1 }] } } } } EOFPatch the Cluster with
spec.topology:1kubectl patch cluster $CLUSTER_NAME --type merge --patch-file cluster-patch.json
Verify the Cluster Was Adopted
Check the state of overall state of the cluster:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9$ clusterctl describe cluster $CLUSTER_NAME NAME READY SEVERITY REASON SINCE MESSAGE Cluster/cc-migration-demo True 8m33s ├─ClusterInfrastructure - DockerCluster/cc-migration-demo True 10m ├─ControlPlane - KubeadmControlPlane/cc-migration-demo-control-plane True 8m33s │ └─Machine/cc-migration-demo-control-plane-knkrs True 8m35s └─Workers └─MachineDeployment/cc-migration-demo-md-0 True 7m40s └─Machine/cc-migration-demo-md-0-7cdf54cd4d-bnqzg True 8m17sVerify the Machines were not recreated:
1 2 3 4$ kubectl get machines -l cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name=$CLUSTER_NAME NAME CLUSTER NODENAME PROVIDERID PHASE AGE VERSION cc-migration-demo-control-plane-knkrs cc-migration-demo cc-migration-demo-control-plane-knkrs docker:////cc-migration-demo-control-plane-knkrs Running 10m v1.25.3 cc-migration-demo-md-0-7cdf54cd4d-bnqzg cc-migration-demo cc-migration-demo-md-0-7cdf54cd4d-bnqzg docker:////cc-migration-demo-md-0-7cdf54cd4d-bnqzg Running 10m v1.25.3Finally, update the Kubernetes version by changing a single value in the Cluster:
1$ kubectl patch cluster $CLUSTER_NAME --type merge --patch '{"spec":{"topology":{"version":"v1.26.0"}}}'
After a few minutes you should see new Machines and updated Nodes. At this point, your Cluster is being managed by the ClusterClass!
